Active Extensor Tendon Stretch | Early Intervention Ergonomics
What is the Active Extensor Tendon Stretch?
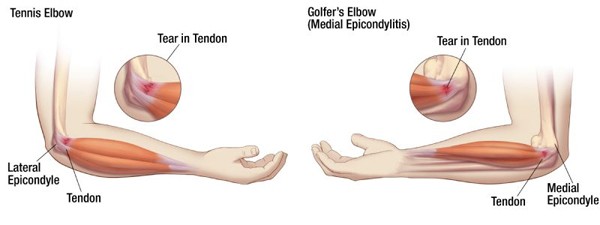
The Active Extensor Tendon Stretch is an excellent stretch to replenish nutrients and re-oxygenate the distal upper extremity. This composite stretch originates at the common wrist extensor tendon of the lateral epicondyle and pulls all the way down to the extensor hood mechanism of the fingers. Perform this stretch to give your body rest when performing forceful gripping, repetitive gripping, awkward or sustained postures of the elbow, forearm, wrist, and hand to prevent common disorders such as tennis elbow, tendinitis, tendinosis, and muscle strain.
This stretch is a type of exercise that targets the extensor muscles in the arms and hands. These muscles are responsible for opening the hand and extending the wrist.
Here’s how to perform an active extensor tendon stretch:
- Sit or stand with good posture, with your arms at your sides and your palms facing inwards.
- Slowly raise your arms out to the side, keeping them straight, until they are level with your shoulders.
- Turn your palms to face the floor, and then slowly extend your wrists so that your fingers point upwards.
- Hold this position for a few seconds, feeling the stretch in your forearms and hands.
- Slowly lower your arms back down to your sides, and then repeat the exercise for several repetitions.
It’s important to perform this exercise slowly and carefully, without over-stretching the muscles. Stop if you feel any pain or discomfort, and don’t force the stretch beyond your limits. You can perform this exercise as part of a warm-up routine before engaging in any activities that require hand and wrist movement, such as sports or typing.
Early Intervention Benefits of this Stretch
Firstly, the Active Extensor Tendon Stretch can help improve grip strength. By stretching the extensor tendons, you can increase the strength of your grip. Additionally, this exercise can reduce the risk of injuries such as tennis elbow and golfer’s elbow, which can be caused by tight extensor tendons.
Moreover, regular practice of the this stretch can increase your range of motion in your wrist and fingers. This benefit is especially useful for athletes and manual laborers. Lastly, if you experience pain in your forearm or wrist, this exercise can help alleviate the pain by loosening tight muscles and tendons.
Overall, the Active Extensor Tendon Stretch is a simple but powerful exercise that can have a significant impact on your forearm, wrist, and hand health.
These early intervention exercises are to improve health and fitness.
It is important to note, if you have an injury or illness, consult with a health care professional before attempting.
Resources
More Tools & Resources from Peak Ergonomics
Contact Us About Reducing Workplace Injuries
Healthy Employees are the Bottom Line! – Learn More!